Stack Memory vs Heap Memory
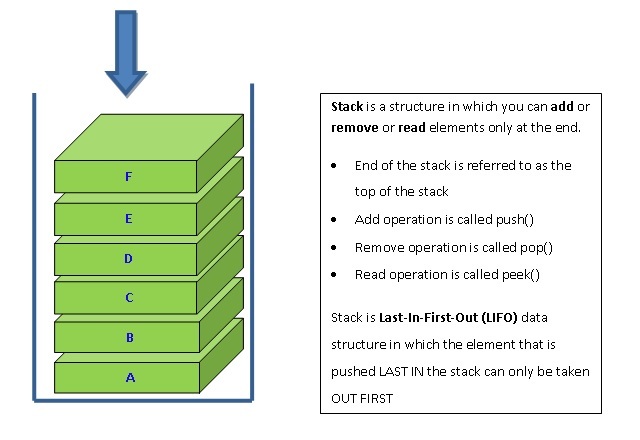
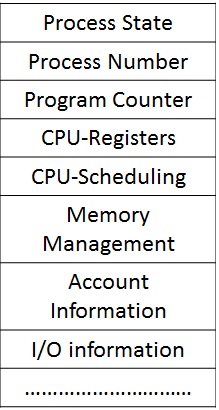
Java runtime uses two types of memory: Stack and Heap. Stack stores value of local primitive variables, local object references (not object values) and method parameters. Static variables, static methods, instance objects and instance methods are stored in the heap as they have to live longer than the stack.
| Stack memory | Heap memory |
|---|---|
| Stack memory has stack of data. That is, data arranged one on top of another | Heap memory has data arranged just like heap of dust. That is, arranged without any order |
| Stack data can be accessed in Last In First Out(LIFO) order. LIFO means what is stored last on the stack can be accessed or removed first from the stack | Heap memory is allocated at any time and deallocated in any order |
| It is simple to track data located in a stack | It is difficult to track data located in a heap |
| Stack memory is limited in size | Heap memory has relatively more memory than in a stack |
| Accessing stack memory is faster | Accessing heap memory is relatively slower |
| Stack is a data structure implemented using simple arrays or a list | Heap is a specialized tree structure implemented using priority queue |
| Stack memory is allocated separately per thread in RAM | Heap memory is allocated and accessible to all processes in RAM |
| When a thread starts, memory allocation is done while execution progresses. When a thread exits, stack memory allocated for a particular thread becomes free | When a process starts, heap memory is allocated. Deallocation happens for unused memory as Garbage collection happens. Complete deallocation can be done only when the process stops |
| Stack memory stores local variables | Heap memory stores objects in Java |
| Stack memory size can be configured using "-Xss <stack size >" option for the java runtime | Heap memory size can be configured using "-Xms <Initial size> -Xmx <Maximum size> " option |
| Stack memory is used for data which needs to be removed when the method exits | Heap is used for Objects which may be needed outside the methods in which memory is allocated first |