Graph Data Structure Types - Directed, Cyclic, Weighted, Connected
Different types of graph exist. Directed acyclic graph, Directed & Undirected graph, Weighted & Unweighted graph, Cyclic graph, Strongly connected graph, Polytree, Forest.
Types of Graph - Based on Direction & Weight
Directed Graph (or) Digraph
Directed Graph is a graph in which each edge has a direction to its successor.
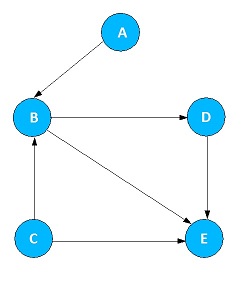
Undirected Graph
Undirected Graph is a graph in which there is no direction on the edges. The flow between two vertices can go in either direction.
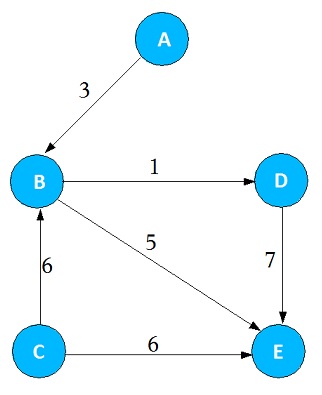
Weighted Graph
If the graph has a some cost or weight on the edge, then we say that graph is said to be a weighted graph. Weight can be applied in both Directed and Undirected graph.
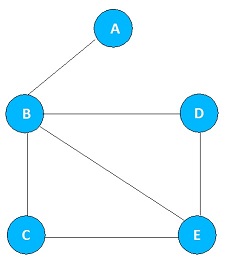
Unweighted Graph
If there is no cost or weight on the edge, then we say that graph is an Unweighted Graph. For example, Figure 2 is the Unweighted Undirected graph
Types of Graph - Based on How Connected the Graph is
Strongly Connected Graph
If there is a path from each vertex to every other vertex in the directed graph, then only we say that directed graph is said to be Strongly connected graph.
Weakly Connected Graph
If there are at least two vertices that are not connected, then we say that directed graph is said to be weakly connected graph.
Disjoint Graph
The graph is a disjoint, if it is not connected.
Complete Graph
If there is an edge between every pair of vertices, then we say that graph is said to be complete graph.
Types of Graph - Based on Cycles
Acyclic Graph
A graph is acyclic if it has no cycles.
Directed Acyclic Graph
A directed acyclic graph is directed graph without any directed cycles. Referred by its short name DAG
PolyTree
PolyTree is a directed graph without any undirected cycles
Forest
Forest is a undirected graph without any cycles









