Graph Data structure - Types, Examples
Next - Types of Graph Data Structure>>
In this page, we will learn about graph data structure, applications of graph, vertices and edges and how graph differs from tree.
Graph is:
- A collection of nodes called vertices and
- A collection of line segments connecting pairs of vertices. In short, line segments are called lines or edges.
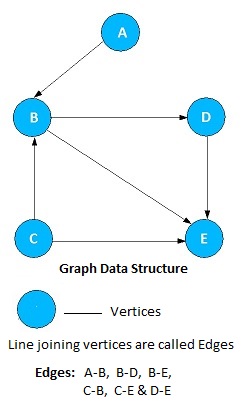
Graph is represented by two sets:
- A set of vertices V. In the above example, Vertices V = {A, B, C, D, E}
- A set of edges E which link the vertices. In the above example, Edges E = { (A,B), (B,D), (B,E), (C,B), (C,E), (D,E) }
Graph G = (V, E)
Each edge is a pair of vertices (v, w), where v,w ∈ V.
Edges are also referred to as a arcs.
Graph Applications
- Graphs are used to represent real life applications.
- Graph can be used to solve complex problems. For example: for designing and routing airline, to route messages over a computer network from one node to another and so on.
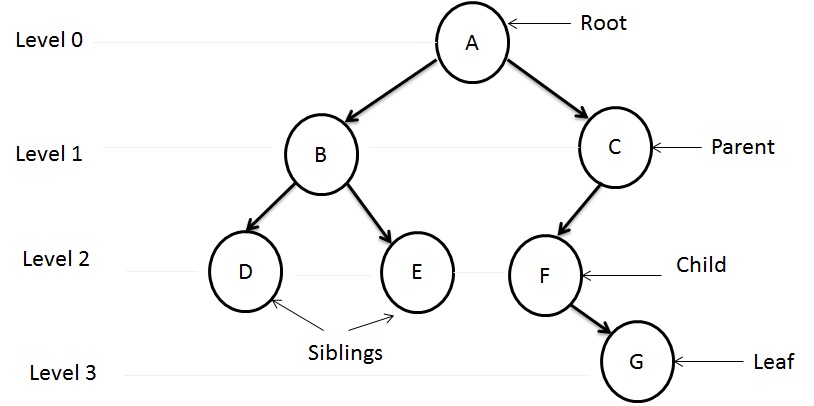
Graph - How it differs from Tree
- Graph and Trees are non-linear data structures.
- In graph, each node can have multiple predecessors as well as multiple successors. In tree, each node can have multiple successors but just one predecessor.
Next - Types of Graph Data Structure>>







