Operating System - Process Control Block
In operating system, each process is represented by a Process control block. The PCB is also known as a task control block. The PCB is a data structure that contains all the information about a particular process.
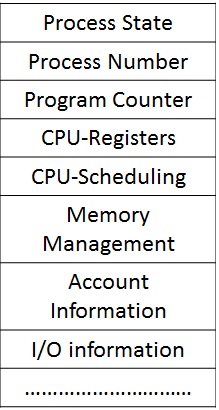
- Process state: current state of the process. It can be any one of the five states (new, ready, running, waiting and terminate).
- Program counter contains address of the next instructions is being to be executed for this process.
- Process number: Unique identification of the process.
- CPU registers: There are different CPU registers that are used by the process during execution.
- CPU-scheduling: contains information about process priority and scheduling.
- Memory management: contains the information of the base and limit register, page table and segment tables, depending on the memory system used by the operating-system.
- Account Information: contains information about the amount of CPU and real time used, time limits, account numbers, job or process numbers, and so on.
- I/O Status Information: contains information of I/O devices allocated to the process, a list of open files, and so on.
In short, PCB acts as the repository of information. This information may vary from process to process.